U.S. military officials have denied recent reports alleging the use of “bunker-buster” bombs against Iranian nuclear facilities, specifically the Fordow site. According to a statement released by U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM), the claims are inaccurate and no such operation occurred. The denial comes amid heightened tensions in the Middle East and ongoing concerns about Iran’s nuclear program.
U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM) refuted claims circulating about the United States employing bunker-buster bombs on Iranian nuclear sites, particularly the Fordow facility, dismissing the reports as false. “These rumors are not true,” a CENTCOM spokesperson affirmed, seeking to quell speculation amidst already strained regional dynamics. The statement was released following reports from various sources suggesting an alleged attack aimed at dismantling or hindering Iran’s nuclear capabilities. The denial underscores the sensitivity surrounding military activities in the region and the potential for misinformation to exacerbate tensions. The claim and subsequent denial occur within a complex geopolitical backdrop, marked by stalled negotiations over Iran’s nuclear program and escalating tensions between Iran and its regional rivals, as well as the United States.
The denial from CENTCOM arrives at a critical juncture. Negotiations aimed at reviving the 2015 nuclear deal, formally known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), remain stalled, with no immediate prospects for resumption. The JCPOA, which offered Iran sanctions relief in exchange for verifiable limits on its nuclear activities, has been in limbo since the U.S. withdrawal in 2018 under the Trump administration. Efforts to revive the agreement under the Biden administration have faced numerous hurdles, including disagreements over the scope of sanctions relief and verification mechanisms.
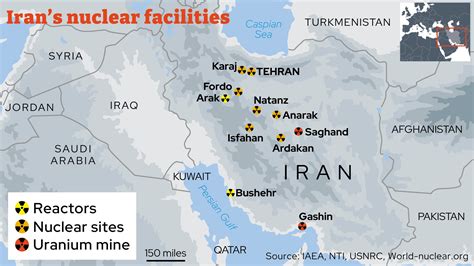
The Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant, located deep under a mountain near the city of Qom, has long been a source of international concern. Its underground location makes it particularly resistant to aerial strikes, hence the significance of reports involving bunker-buster bombs, which are specifically designed to penetrate hardened targets. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has consistently monitored the Fordow facility, raising concerns about Iran’s enrichment activities there. In recent years, Iran has increased its enrichment levels, exceeding the limits set by the JCPOA.
“The U.S. military is committed to ensuring the security and stability of the region,” the CENTCOM statement added, reiterating its dedication to working with partners to counter threats and maintain a strong presence. This commitment is particularly relevant given the ongoing conflicts and proxy wars in the Middle East, where Iran plays a significant role. The U.S. maintains a network of military bases and partnerships throughout the region, aimed at deterring aggression and ensuring freedom of navigation in vital waterways.
The denial also highlights the importance of verifying information in an era of widespread social media and online news sources. False reports and rumors can quickly spread, leading to confusion and potentially escalating tensions. Official statements from credible sources, such as CENTCOM, are crucial in dispelling misinformation and providing accurate information to the public.
Analysis of the Geopolitical Context
The denial of the alleged bunker-buster strike occurs within a broader context of escalating tensions and strategic maneuvering in the Middle East. Several factors contribute to this heightened state of alert:
- Stalled Nuclear Negotiations: The failure to revive the JCPOA has created a vacuum, allowing Iran to advance its nuclear program without the constraints imposed by the agreement. This has raised concerns among Western powers and regional rivals, who fear that Iran is moving closer to developing a nuclear weapon.
- Regional Proxy Conflicts: Iran is involved in numerous proxy conflicts throughout the Middle East, supporting armed groups in countries such as Yemen, Syria, and Lebanon. These conflicts have fueled instability and exacerbated sectarian tensions. The U.S. and its allies, particularly Saudi Arabia and Israel, view Iran’s regional activities as a major threat.
- Increased Iranian Enrichment: Iran’s decision to increase its uranium enrichment levels has further heightened concerns about its nuclear ambitions. The IAEA has reported that Iran is enriching uranium to levels far beyond those needed for peaceful purposes, raising fears that it is seeking to develop weapons-grade material.
- Naval Tensions: The Persian Gulf and surrounding waterways have been the site of numerous incidents involving Iranian and U.S. naval forces. These incidents, often involving close encounters and accusations of harassment, have raised the risk of miscalculation and escalation.
- Cyber Warfare: Cyberattacks have become an increasingly common tool of statecraft, and Iran has been accused of conducting cyberattacks against U.S. and Israeli targets. These attacks can disrupt critical infrastructure and sow discord, further destabilizing the region.
- Internal Iranian Dynamics: Domestic factors within Iran, including economic challenges and political infighting, also play a role in shaping its foreign policy. Hardline elements within the Iranian regime may seek to escalate tensions with the U.S. and its allies in order to consolidate their power and deflect attention from internal problems.
- U.S. Elections: The upcoming U.S. presidential election adds another layer of complexity to the situation. Different administrations could adopt very different approaches to dealing with Iran, creating uncertainty and potentially incentivizing Iran to take provocative actions.
The Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant: A Strategic Asset and Point of Contention
The Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant is a critical component of Iran’s nuclear program and a significant point of contention in international negotiations. Its underground location makes it highly resistant to air strikes, which is why rumors of a bunker-buster attack are so sensitive. Here’s a more detailed look at the facility:
- Location and Design: The Fordow plant is located approximately 32 kilometers (20 miles) northeast of the city of Qom, buried deep inside a mountain. The facility was built in secret and was only revealed to the IAEA in 2009. Its design is intended to protect it from aerial bombardment, making it a particularly challenging target.
- Enrichment Activities: The Fordow plant is used to enrich uranium, a key step in the production of nuclear fuel or, potentially, nuclear weapons. Iran has repeatedly stated that its enrichment activities are solely for peaceful purposes, such as generating electricity and producing medical isotopes. However, Western powers and their allies are skeptical of these claims, arguing that Iran’s enrichment program has no credible civilian justification.
- IAEA Monitoring: The IAEA has been monitoring the Fordow plant under various agreements, including the JCPOA. However, Iran has at times restricted IAEA access to the facility, raising concerns about its transparency and cooperation.
- JCPOA Restrictions: Under the JCPOA, Iran agreed to limit its enrichment activities at Fordow and to convert the facility to a research center. However, after the U.S. withdrew from the JCPOA, Iran began to roll back its commitments, including resuming enrichment at Fordow.
- Military Significance: The Fordow plant’s location and design make it a potentially valuable asset in a military conflict. If Iran were to develop nuclear weapons, the Fordow plant could be used to produce the necessary fissile material. Its hardened structure would make it difficult to destroy in a conventional military strike.
Bunker-Buster Bombs: Capabilities and Concerns
Bunker-buster bombs, also known as earth-penetrating weapons, are designed to destroy hardened targets such as underground bunkers and command centers. These weapons typically use a combination of high explosive warheads and specialized fusing mechanisms to penetrate deep into the ground before detonating.
- Types of Bunker-Busters: There are several types of bunker-buster bombs in use around the world. The U.S. military uses the GBU-28 and the Massive Ordnance Penetrator (MOP), which are among the most powerful bunker-busters in existence. These bombs are designed to penetrate several meters of reinforced concrete before detonating, allowing them to destroy even the most heavily protected underground facilities.
- Concerns About Use: The use of bunker-buster bombs raises several concerns. First, these weapons can cause significant collateral damage, particularly in urban areas. The deep penetration and powerful explosions can damage nearby buildings and infrastructure, potentially causing civilian casualties. Second, the use of bunker-busters can escalate conflicts. The destruction of critical infrastructure, such as command and control centers, can provoke a strong response from the targeted country. Finally, the proliferation of bunker-buster technology is a concern. As more countries develop these weapons, the risk of their use in future conflicts increases.
- Effectiveness: The effectiveness of bunker-buster bombs depends on several factors, including the type of bomb used, the depth and construction of the target, and the accuracy of the delivery system. Even the most powerful bunker-busters may not be able to destroy all underground facilities, particularly those that are very deep or heavily reinforced.
U.S. Military Presence in the Middle East: A Deterrent or a Provocation?
The U.S. maintains a significant military presence in the Middle East, including bases, ships, and aircraft. This presence is intended to deter aggression, protect U.S. interests, and ensure regional stability. However, it is also viewed by some as a provocation, particularly by Iran and its allies.
- Strategic Importance: The Middle East is strategically important to the U.S. for several reasons. First, the region is a major source of oil and gas, which are vital to the global economy. Second, the Middle East is a key transit route for trade and commerce. Third, the region is home to several U.S. allies, including Israel, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan.
- Military Assets: The U.S. military maintains a wide range of assets in the Middle East, including naval bases in Bahrain and Qatar, air bases in Qatar and the United Arab Emirates, and army bases in Kuwait and Iraq. The U.S. Navy’s Fifth Fleet is based in Bahrain, and the U.S. Air Force maintains a significant presence at Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar.
- Deterrence and Stability: The U.S. military presence in the Middle East is intended to deter aggression by Iran and other regional actors. The U.S. also works with its allies to maintain stability in the region, including providing military assistance and conducting joint exercises.
- Criticisms: The U.S. military presence in the Middle East has been criticized by some for fueling anti-American sentiment and contributing to regional instability. Critics argue that the U.S. presence is seen as an occupation by many in the region and that it has emboldened authoritarian regimes. Others argue that the U.S. presence is necessary to counter Iranian influence and protect U.S. interests.
Potential Implications of Military Action Against Iran
Any military action against Iran, including a strike on its nuclear facilities, would have far-reaching implications for the region and the world.
- Escalation of Conflict: A military strike could trigger a wider conflict, drawing in other countries and armed groups. Iran could retaliate against U.S. forces and allies in the region, as well as launching attacks on shipping in the Persian Gulf.
- Regional Instability: A conflict with Iran could further destabilize the already volatile Middle East. It could exacerbate existing conflicts and create new ones, leading to a humanitarian crisis and mass displacement.
- Economic Disruption: A conflict in the Middle East could disrupt oil supplies and raise prices, impacting the global economy. It could also disrupt trade and investment, leading to economic downturn.
- Nuclear Proliferation: A military strike on Iran’s nuclear facilities could prompt Iran to accelerate its efforts to develop nuclear weapons. It could also encourage other countries in the region to pursue nuclear weapons, leading to a nuclear arms race.
- International Condemnation: A military strike against Iran would likely be condemned by many countries, even if it were carried out with the support of some U.S. allies. It could damage U.S. credibility and isolate the U.S. on the world stage.
Diplomatic Efforts: The Path Forward?
Given the risks and potential consequences of military action, diplomatic efforts remain the preferred approach for resolving the Iranian nuclear issue.
- Reviving the JCPOA: Efforts to revive the JCPOA are ongoing, but face significant challenges. The U.S. and Iran remain far apart on key issues, including sanctions relief and verification mechanisms.
- Alternative Frameworks: If the JCPOA cannot be revived, alternative frameworks may need to be explored. These could include a new agreement that addresses the concerns of all parties, or a more limited agreement that focuses on specific aspects of Iran’s nuclear program.
- Regional Dialogue: A broader regional dialogue, involving Iran and its neighbors, could help to address the underlying tensions and security concerns that fuel the nuclear issue. This dialogue could focus on issues such as arms control, maritime security, and regional conflict resolution.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is essential for addressing the Iranian nuclear issue. The U.S., Europe, Russia, and China all have a role to play in encouraging Iran to comply with its international obligations and in promoting regional stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Did the U.S. actually use bunker-buster bombs on Iran’s Fordow nuclear site?
- No. According to a statement released by U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM), reports of the U.S. using bunker-buster bombs on Iranian nuclear facilities, particularly the Fordow site, are false. “These rumors are not true,” stated a CENTCOM spokesperson.
-
What are bunker-buster bombs and why are they significant in this context?
- Bunker-buster bombs, also known as earth-penetrating weapons, are designed to destroy hardened targets such as underground bunkers and command centers. The Fordow facility’s location deep inside a mountain makes it a potential target for such weapons, hence the sensitivity of reports involving their alleged use. They use a combination of high explosive warheads and specialized fusing mechanisms to penetrate deep into the ground before detonating.
-
Why is the Fordow nuclear site a concern for the U.S. and international community?
- The Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant is located deep under a mountain, making it resistant to aerial strikes. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) has consistently monitored the facility, raising concerns about Iran’s enrichment activities there. Iran has increased its enrichment levels, exceeding the limits set by the JCPOA. Its underground location, coupled with enrichment activities, raises concerns about potential military applications.
-
What is the current status of the JCPOA and how does it relate to this situation?
- Negotiations aimed at reviving the 2015 nuclear deal, formally known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), remain stalled, with no immediate prospects for resumption. The JCPOA, which offered Iran sanctions relief in exchange for verifiable limits on its nuclear activities, has been in limbo since the U.S. withdrawal in 2018. The stalled negotiations contribute to heightened tensions, as Iran advances its nuclear program without JCPOA constraints.
-
What are the potential implications of military action against Iranian nuclear facilities?
- Military action against Iran could have far-reaching and severe consequences, including escalation of regional conflicts, significant economic disruption, and a potential acceleration of nuclear proliferation in the Middle East. It could also trigger retaliation against U.S. forces and allies in the region. Widespread international condemnation and damage to U.S. credibility are also likely. Given these severe risks, diplomatic solutions are generally preferred.
Conclusion
The denial by U.S. Central Command of the alleged use of bunker-buster bombs against Iran’s Fordow nuclear facility underscores the delicate and volatile situation in the Middle East. While the immediate reports appear to be unfounded, they highlight the ongoing concerns about Iran’s nuclear program, the stalled JCPOA negotiations, and the potential for miscalculation and escalation in the region. The incident serves as a reminder of the importance of verifying information, maintaining open channels of communication, and pursuing diplomatic solutions to address the complex challenges facing the Middle East. The persistent tensions necessitate continuous vigilance and a commitment to de-escalation strategies to prevent a potentially catastrophic conflict. A misstep could have cascading consequences for the region and the world.