Rare earth minerals, crucial for technologies ranging from smartphones to electric vehicles and defense systems, are emerging as a key battleground in the ongoing US-China trade relationship and a critical element in the global tech race. The United States is heavily reliant on China for the processing of these materials, creating both economic and national security vulnerabilities.
The dependence of the U.S. on China for rare earth minerals is a complex issue with deep historical roots and significant implications for the future of technology and geopolitics. Rare earth elements (REEs) are a set of seventeen metallic elements that are vital components in a wide array of modern technologies. These include smartphones, wind turbines, electric vehicles, medical devices, and defense systems, such as missile guidance and radar systems. Their unique magnetic, catalytic, and optical properties make them indispensable in these applications.
The Extent of U.S. Dependence
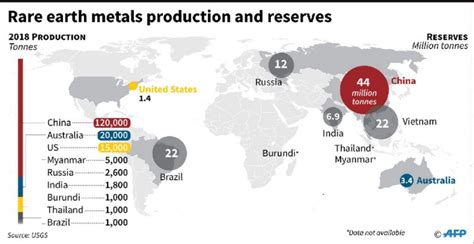
The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) has documented the extent of U.S. reliance on foreign sources for rare earth minerals. While the U.S. does have some domestic mining operations, the vast majority of rare earth processing and refining occurs in China. This dependence has raised concerns about supply chain vulnerabilities and potential geopolitical leverage.
“Rare earth minerals are crucial for everything from electric vehicles to national defense,” the original source noted, emphasizing the broad impact of these materials.
Historical Context: China’s Dominance
China’s dominance in the rare earth market did not happen overnight. In the late 20th century, China strategically invested in rare earth mining and processing technologies, often at lower costs than could be sustained in other countries due to differences in labor costs and environmental regulations. As a result, China became the world’s leading producer and processor of rare earth elements, capturing a significant market share.
During this period, the U.S. and other Western countries gradually reduced their domestic rare earth production, partly due to environmental concerns associated with mining and processing, as well as the economic competitiveness of Chinese producers. This shift left the U.S. increasingly reliant on China for these critical materials.
Economic Implications
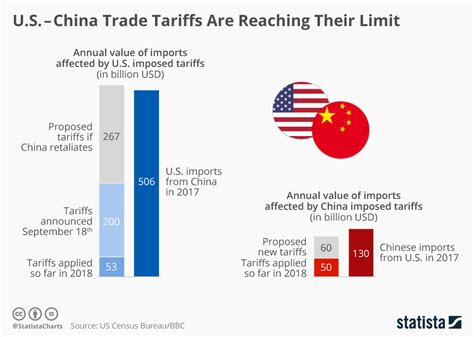
The economic implications of this dependence are substantial. The U.S. imports billions of dollars worth of rare earth minerals and products containing rare earths from China annually. This trade imbalance creates economic vulnerabilities, particularly in sectors that rely heavily on these materials, such as electronics, automotive, and defense industries.
Moreover, the concentration of rare earth processing in China gives Beijing significant leverage over global supply chains. Any disruption in the supply of rare earth elements, whether due to trade disputes, geopolitical tensions, or domestic policies, could have far-reaching consequences for U.S. industries and consumers.
National Security Concerns
Beyond economic considerations, the U.S. dependence on China for rare earth minerals also raises critical national security concerns. The defense industry relies on rare earth elements for the production of advanced weapons systems and military technologies. A disruption in the supply of these materials could impair the U.S. military’s ability to maintain its technological edge and respond to security threats.
The U.S. Department of Defense has identified rare earth minerals as critical materials and has taken steps to diversify its supply chains and reduce its reliance on China. However, these efforts are still in their early stages, and significant challenges remain.
Efforts to Diversify Supply Chains
Recognizing the risks associated with its dependence on China, the U.S. government has been actively pursuing strategies to diversify its rare earth supply chains. These efforts include:
-
Investing in Domestic Mining and Processing: The U.S. government has provided funding and incentives for the development of domestic rare earth mining and processing facilities. The goal is to increase domestic production capacity and reduce reliance on foreign sources.
-
Supporting International Partnerships: The U.S. is working with allies and partners around the world to develop alternative sources of rare earth minerals. This includes collaborating with countries such as Australia, Canada, and Japan to establish secure and resilient supply chains.
-
Promoting Recycling and Innovation: The U.S. is also investing in research and development to improve rare earth recycling technologies and find alternative materials that can replace rare earths in certain applications. This could help reduce demand for newly mined rare earth elements and promote a more circular economy.
-
Government Initiatives: Several government initiatives, such as the establishment of the Critical Minerals Working Group and the implementation of the National Defense Authorization Act, aim to address the challenges posed by U.S. dependence on China for rare earth minerals.
Challenges and Obstacles
Despite these efforts, diversifying rare earth supply chains is a complex and challenging undertaking. Some of the obstacles include:
-
Environmental Regulations: Rare earth mining and processing can have significant environmental impacts, including water pollution, soil contamination, and habitat destruction. Stricter environmental regulations in the U.S. can make it more difficult and costly to develop domestic rare earth projects.
-
Technological Barriers: Processing rare earth minerals is a complex and technically challenging process. The U.S. needs to invest in research and development to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly processing technologies.
-
Economic Competitiveness: Chinese rare earth producers often have lower production costs due to differences in labor costs, environmental regulations, and government subsidies. The U.S. needs to find ways to make its domestic rare earth industry more economically competitive.
-
Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes can complicate efforts to diversify rare earth supply chains. The U.S. needs to work closely with its allies and partners to navigate these challenges and ensure a stable and secure supply of rare earth minerals.
The Tech Race and Rare Earths
The importance of rare earth minerals extends beyond traditional industries and is increasingly tied to the global tech race. These materials are essential for the development of advanced technologies such as:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Rare earth magnets are used in the motors of electric vehicles, providing high power and efficiency.
- Renewable Energy: Rare earth elements are used in wind turbines and solar panels, helping to generate clean energy.
- Electronics: Rare earth minerals are used in smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices.
- Defense Systems: Rare earth elements are used in missile guidance systems, radar systems, and other military technologies.
As countries compete to develop and deploy these technologies, access to rare earth minerals becomes a strategic imperative. China’s dominance in the rare earth market gives it a significant advantage in the tech race. The U.S. and other countries need to secure their own supply of rare earth minerals to remain competitive and ensure their technological leadership.
The Role of Innovation
Innovation plays a crucial role in addressing the challenges posed by rare earth dependence. This includes:
- Developing Alternative Materials: Researchers are exploring alternative materials that can replace rare earths in certain applications. This could reduce demand for rare earth minerals and mitigate supply chain risks.
- Improving Recycling Technologies: Recycling rare earth elements from electronic waste and other sources can help reduce the need for newly mined materials.
- Enhancing Mining and Processing Techniques: Developing more efficient and environmentally friendly mining and processing techniques can help reduce the environmental impact of rare earth production.
Geopolitical Implications and Trade Dynamics
The rare earth issue has become a focal point in the broader geopolitical competition between the U.S. and China. The U.S. views China’s dominance in the rare earth market as a strategic vulnerability and is taking steps to reduce its dependence. China, on the other hand, sees its rare earth industry as a source of economic and political power.
The potential for China to restrict rare earth exports as a form of economic coercion is a significant concern for the U.S. and other countries. This has led to calls for greater diversification of supply chains and the development of alternative sources of rare earth minerals.
Trade dynamics surrounding rare earths are complex and evolving. The U.S. has imposed tariffs on certain Chinese imports, including rare earth products, in an effort to level the playing field. However, these tariffs have also raised costs for U.S. manufacturers and consumers.
Future Outlook
The future of the rare earth market is uncertain. The U.S. is likely to continue its efforts to diversify its supply chains and reduce its dependence on China. However, these efforts will take time and require significant investment.
China is likely to remain a dominant player in the rare earth market for the foreseeable future. However, its market share may gradually decline as other countries develop their own rare earth industries.
The global tech race will continue to drive demand for rare earth minerals. Countries that can secure access to these materials will have a competitive advantage in the development and deployment of advanced technologies.
Environmental Considerations
It is crucial to emphasize the environmental considerations associated with rare earth mining and processing. Traditional methods can lead to significant environmental damage, including:
- Water Pollution: Mining and processing activities can release harmful chemicals and pollutants into waterways, contaminating drinking water and harming aquatic ecosystems.
- Soil Contamination: Rare earth mining can disrupt soil stability and release toxic substances into the soil, making it unsuitable for agriculture and other uses.
- Air Pollution: Processing rare earth minerals can release harmful air pollutants, contributing to respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Habitat Destruction: Mining operations can destroy natural habitats and displace wildlife.
To mitigate these environmental impacts, it is essential to adopt sustainable mining and processing practices, including:
- Implementing Strict Environmental Regulations: Governments should enforce strict environmental regulations to ensure that rare earth mining and processing activities are conducted in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Investing in Green Technologies: Research and development should focus on developing more environmentally friendly mining and processing technologies that minimize pollution and waste.
- Promoting Recycling: Recycling rare earth elements from electronic waste and other sources can help reduce the need for newly mined materials and minimize environmental impacts.
- Restoring Damaged Ecosystems: Mining companies should be required to restore damaged ecosystems after mining operations are completed.
Economic Strategies and Policy Implications
The economic strategies to counter China’s dominance in rare earths involve multifaceted approaches, including government incentives, private sector investments, and international collaborations. The U.S. government has implemented policies to encourage domestic production through tax breaks, subsidies, and streamlined permitting processes. For instance, the Department of Defense has awarded contracts to companies to develop domestic rare earth processing facilities.
Private sector investments are equally crucial. Companies are investing in new mining projects and processing technologies to enhance domestic capacity. Collaboration with international partners, such as Australia and Canada, aims to diversify supply chains and reduce reliance on a single source. Trade agreements and strategic alliances can further solidify these partnerships, ensuring a stable and secure supply of rare earth minerals.
From a policy perspective, the U.S. government is considering stockpiling rare earth minerals to buffer against potential supply disruptions. Additionally, policies supporting research and development in alternative materials and recycling technologies can reduce the long-term demand for newly mined rare earths.
The Impact on Technological Innovation
The availability of rare earth minerals directly impacts technological innovation. These elements are essential for producing high-performance magnets used in electric vehicles, wind turbines, and various electronic devices. Limited access to rare earths can hinder the development and deployment of these technologies, affecting the competitiveness of industries relying on them.
Securing a stable supply of rare earths is thus crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in technological advancements. Countries that can ensure access to these materials are better positioned to lead in sectors such as renewable energy, electric mobility, and advanced electronics.
Geopolitical Strategies to Counter China’s Influence
Geopolitical strategies to counter China’s influence in the rare earth market involve building alliances and diversifying supply sources. The U.S. is actively engaging with countries like Australia, Canada, and Japan to establish alternative supply chains. These partnerships aim to reduce dependence on China and create a more balanced global market.
Another strategy involves promoting transparency and fair competition in the rare earth market. This includes advocating for international standards on mining and processing practices to ensure environmental sustainability and prevent unfair trade practices. Diplomatic efforts to address geopolitical tensions and resolve trade disputes can also contribute to a more stable and predictable rare earth market.
The Role of International Cooperation
International cooperation is vital for addressing the challenges posed by the rare earth issue. Collaborative efforts among countries can facilitate the sharing of best practices, technological innovations, and financial resources. International organizations, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO), can play a role in promoting fair trade and resolving disputes related to rare earth minerals.
Joint research projects and development initiatives can accelerate the development of alternative materials and recycling technologies. Additionally, coordinated efforts to establish secure and diversified supply chains can enhance the resilience of the global economy to supply disruptions.
Future Trends and Predictions
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of the rare earth market. Demand for rare earth minerals is expected to continue growing, driven by the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, renewable energy technologies, and advanced electronics. This growing demand will put pressure on existing supply chains and further highlight the importance of diversification.
Technological innovations in mining, processing, and recycling are expected to improve the efficiency and sustainability of rare earth production. The development of alternative materials could also reduce the long-term demand for rare earths.
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes are likely to remain a factor in the rare earth market. Countries will continue to pursue strategies to secure their access to these critical materials and reduce their dependence on dominant suppliers. International cooperation and diplomatic efforts will be essential for managing these challenges and ensuring a stable and sustainable rare earth market.
The U.S. must act decisively to secure its rare earth supply chains to maintain its economic and national security interests in an increasingly competitive global landscape. Failure to do so risks ceding a crucial strategic advantage to China.
FAQ Section
1. Why are rare earth minerals considered “rare”?
Rare earth minerals are not necessarily rare in terms of their abundance in the Earth’s crust. The term “rare” refers to the fact that these minerals are typically found in low concentrations and are often difficult and costly to extract and process.
2. What makes rare earth minerals so important for modern technology?
Rare earth elements possess unique magnetic, catalytic, and optical properties that make them essential components in a wide range of modern technologies. These include smartphones, wind turbines, electric vehicles, medical devices, and defense systems.
3. How reliant is the United States on China for rare earth minerals?
The United States is heavily reliant on China for the processing of rare earth minerals. While the U.S. has some domestic mining operations, the vast majority of rare earth processing and refining occurs in China, creating economic and national security vulnerabilities.
4. What steps is the U.S. government taking to reduce its dependence on China for rare earth minerals?
The U.S. government is pursuing several strategies to diversify its rare earth supply chains, including investing in domestic mining and processing, supporting international partnerships, promoting recycling and innovation, and implementing government initiatives such as the Critical Minerals Working Group.
5. What are the environmental concerns associated with rare earth mining and processing?
Rare earth mining and processing can have significant environmental impacts, including water pollution, soil contamination, air pollution, and habitat destruction. To mitigate these impacts, it is essential to adopt sustainable mining and processing practices and enforce strict environmental regulations.