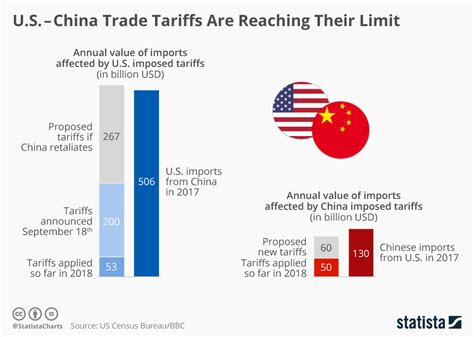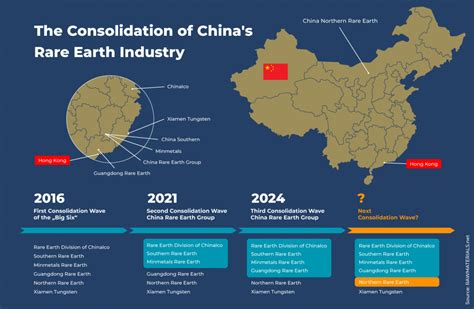
The escalating trade rivalry between the U.S. and China has brought rare earth minerals, essential components in numerous high-tech applications, into sharp focus, highlighting their pivotal role in the future of technology and potentially reshaping global trade dynamics.
Rare earth elements (REEs), a collection of 17 metallic elements, are critical in manufacturing everything from smartphones and electric vehicles to wind turbines and defense systems. As the demand for these technologies surges, so does the strategic importance of REEs, positioning them as a key battleground in the U.S.-China trade landscape. “Rare earth minerals are crucial to so many technologies that we depend on every day,” explains Yahoo Finance’s Pras Subramanian.
China currently dominates the rare earth mineral supply chain, controlling a significant portion of both mining and processing operations. This dominance has raised concerns in the U.S. and other nations about over-reliance on a single source, particularly given the ongoing geopolitical tensions. The U.S. is actively seeking to diversify its supply chains and reduce its dependence on China for these critical materials.
China’s Dominance and Global Concerns
China’s dominance in the rare earth market is not a recent phenomenon. Over the past few decades, China has strategically invested in developing its rare earth mining and processing capabilities, allowing it to undercut competitors and establish itself as the world’s leading supplier. This strategic advantage gives China significant leverage in global trade and technology.
The concerns surrounding China’s dominance are multifaceted. Firstly, there is the risk of supply disruptions. Should geopolitical tensions escalate, China could potentially restrict or halt exports of REEs, crippling industries that rely on these materials. Secondly, there are concerns about pricing. China’s control over the market allows it to manipulate prices, potentially disadvantaging companies and countries that are dependent on its supply. Thirdly, environmental concerns associated with rare earth mining and processing have also been raised. China’s environmental standards have historically been less stringent than those in other countries, leading to environmental degradation in some mining regions.
U.S. Efforts to Reduce Dependence
Recognizing the risks associated with relying heavily on China, the U.S. government and private sector are taking steps to reduce this dependence. These efforts include:
- Investing in Domestic Mining and Processing: The U.S. is investing in the development of its own rare earth mining and processing capabilities. This includes funding research and development, providing financial incentives for companies to establish domestic operations, and streamlining the permitting process for new mines and processing facilities.
- Diversifying Supply Chains: The U.S. is actively seeking to diversify its supply chains by sourcing REEs from other countries, such as Australia, Canada, and Brazil. This involves establishing partnerships with these countries and providing financial and technical assistance to help them develop their rare earth industries.
- Recycling and Reusing REEs: Recycling and reusing REEs from electronic waste and other sources is another strategy being pursued. This can help to reduce the demand for newly mined REEs and lessen the environmental impact of rare earth production.
- Developing Alternative Materials: Research is underway to develop alternative materials that can be used in place of REEs in certain applications. This could significantly reduce the demand for REEs and mitigate the risks associated with supply disruptions.
- Government Initiatives and Policies: The U.S. government has implemented various policies and initiatives to support the development of a domestic rare earth industry. These include the establishment of the Critical Minerals Working Group, which is tasked with developing a national strategy for ensuring a secure and reliable supply of critical minerals, including REEs.
Impact on Tech Industry and Future Outlook
The availability and cost of REEs have a direct impact on the tech industry. These minerals are essential components in a wide range of technologies, including smartphones, computers, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. Any disruption in the supply of REEs or increase in their prices could lead to higher costs for these products and potentially slow down innovation.
The future of the rare earth market is uncertain. China is likely to remain a major player for the foreseeable future, but the U.S. and other countries are making significant efforts to reduce their dependence on China. The development of new mining and processing capabilities, the diversification of supply chains, and the development of alternative materials could all help to create a more balanced and resilient rare earth market.
The U.S.-China trade rivalry is likely to continue to shape the rare earth market. As both countries compete for technological and economic dominance, the control of rare earth resources will become increasingly important. This could lead to further investments in domestic mining and processing, as well as efforts to secure access to rare earth resources from other countries.
Environmental Concerns
Rare earth mining and processing can have significant environmental impacts. The extraction of REEs often involves the use of harsh chemicals, which can contaminate soil and water. The processing of REEs can also generate large amounts of waste, including radioactive materials.
Efforts are being made to mitigate the environmental impacts of rare earth production. These include developing more environmentally friendly mining and processing techniques, implementing stricter environmental regulations, and promoting the recycling and reuse of REEs.
“One of the big problems with rare earth mining is it’s really dirty, environmentally speaking,” notes Yahoo Finance’s Pras Subramanian. This highlights the importance of sustainable practices in rare earth production.
Geopolitical Implications
The control of rare earth resources has significant geopolitical implications. Countries that control these resources have a strategic advantage in the global economy. They can use this advantage to influence trade policy, promote their own industries, and exert political pressure on other countries.
The U.S. is seeking to counter China’s geopolitical influence by developing its own rare earth industry and diversifying its supply chains. This is seen as essential for ensuring U.S. economic and national security.
Economic Impact
The rare earth industry has a significant economic impact. It creates jobs in mining, processing, manufacturing, and research and development. It also contributes to economic growth by supporting the development of new technologies and industries.
The U.S. is hoping to revitalize its domestic rare earth industry and create new jobs in these sectors. This is seen as a way to boost the U.S. economy and reduce its dependence on foreign suppliers.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are playing a key role in the rare earth industry. New technologies are being developed to improve the efficiency of mining and processing, reduce the environmental impact of rare earth production, and develop alternative materials that can be used in place of REEs.
These technological advancements are essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of the rare earth industry. They can help to reduce costs, improve environmental performance, and create new opportunities for innovation.
The Role of Innovation
Innovation is critical to addressing the challenges and opportunities in the rare earth market. This includes innovation in mining and processing techniques, recycling technologies, and the development of alternative materials.
Companies and researchers are actively working on innovative solutions to these challenges. Their efforts could lead to a more sustainable, resilient, and competitive rare earth market.
The Future of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a major driver of demand for rare earth minerals. REEs are used in the magnets that power EV motors, as well as in the batteries that store energy.
As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the demand for REEs is also expected to increase. This will put further pressure on the rare earth supply chain and could lead to higher prices for these materials.
“Electric vehicles are really a big part of the story for rare earth minerals,” confirms Yahoo Finance’s Pras Subramanian, underscoring the link between EV adoption and REE demand.
The Impact on Renewable Energy
Renewable energy technologies, such as wind turbines and solar panels, also rely on rare earth minerals. REEs are used in the magnets that generate electricity in wind turbines, as well as in the semiconductors that convert sunlight into electricity in solar panels.
The growth of the renewable energy sector is also expected to drive demand for REEs. This will further increase the strategic importance of these materials and could lead to increased competition for their supply.
The Importance of Recycling
Recycling rare earth minerals is becoming increasingly important. Recycling can help to reduce the demand for newly mined REEs and lessen the environmental impact of rare earth production.
Efforts are being made to develop more efficient and cost-effective recycling technologies. These technologies could play a key role in ensuring a sustainable supply of REEs in the future.
The Role of Government Regulation
Government regulation plays a significant role in the rare earth industry. Regulations can help to ensure that mining and processing operations are conducted in an environmentally responsible manner, that workers are protected, and that companies are held accountable for their actions.
The U.S. government is considering implementing stricter regulations on the rare earth industry. These regulations could help to level the playing field for U.S. companies and ensure that rare earth production is sustainable.
The Consumer Perspective
Consumers are increasingly aware of the importance of rare earth minerals and the challenges associated with their supply. Consumers are also becoming more interested in purchasing products that are made with recycled materials or that are designed to be easily recycled.
Consumer demand for sustainable products could help to drive innovation in the rare earth industry and promote the development of more environmentally friendly mining and processing practices.
International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential for addressing the challenges in the rare earth market. Countries need to work together to diversify supply chains, develop common environmental standards, and promote the recycling and reuse of REEs.
The U.S. is working with its allies to strengthen international cooperation on rare earth issues. This includes sharing information, coordinating policies, and providing financial and technical assistance to developing countries.
The Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for the rare earth market is uncertain. However, it is clear that these materials will continue to be strategically important for many years to come.
The U.S. and other countries are making significant investments in developing their own rare earth industries and diversifying their supply chains. These efforts could help to create a more balanced and resilient rare earth market in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What are rare earth elements (REEs)?
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a set of 17 metallic elements that are critical components in many modern technologies, including smartphones, electric vehicles, wind turbines, and defense systems. They are not necessarily “rare” in terms of abundance in the Earth’s crust, but they are rarely found in concentrated deposits, making them economically challenging to mine.
-
Why are rare earth minerals so important?
REEs possess unique magnetic, catalytic, and optical properties that make them essential for various high-tech applications. For example, neodymium is used in powerful magnets for electric vehicle motors and wind turbine generators, while lanthanum is used in camera lenses and hybrid vehicle batteries. Without REEs, the performance and efficiency of many modern technologies would be significantly compromised.
-
Why is China the dominant player in the rare earth market?
China has strategically invested in developing its rare earth mining and processing capabilities over the past few decades. This includes providing financial incentives, streamlining regulations, and investing in research and development. As a result, China now controls a significant portion of the global rare earth supply chain, including both mining and refining.
-
What is the U.S. doing to reduce its dependence on China for rare earths?
The U.S. is pursuing several strategies to reduce its dependence on China for rare earths, including:
- Investing in domestic mining and processing facilities.
- Diversifying supply chains by sourcing REEs from other countries.
- Promoting the recycling and reuse of REEs from electronic waste.
- Funding research and development of alternative materials that can replace REEs in certain applications.
- Implementing government policies to support the development of a domestic rare earth industry.
-
What are the environmental concerns associated with rare earth mining and processing?
Rare earth mining and processing can have significant environmental impacts, including:
- Contamination of soil and water from the use of harsh chemicals.
- Generation of large amounts of waste, including radioactive materials.
- Deforestation and habitat destruction.
- Air pollution from dust and emissions. Efforts are being made to mitigate these impacts by developing more environmentally friendly mining and processing techniques, implementing stricter environmental regulations, and promoting the recycling and reuse of REEs.
-
How does the U.S.-China trade rivalry impact the rare earth market?
The U.S.-China trade rivalry has brought rare earth minerals into sharp focus, highlighting their strategic importance. As both countries compete for technological and economic dominance, the control of rare earth resources becomes increasingly crucial. This leads to potential trade restrictions, price fluctuations, and increased investment in securing alternative sources of rare earths. The rivalry also encourages innovation in recycling and the development of substitute materials to reduce dependence on either nation’s supply.
-
What role do electric vehicles (EVs) play in the demand for rare earth minerals?
Electric vehicles are a significant driver of demand for rare earth minerals, particularly neodymium and dysprosium, which are used in the permanent magnets of EV motors. As the global adoption of EVs increases, so does the demand for these minerals, placing greater pressure on the supply chain and potentially leading to price increases. The link between EV production and rare earth mineral demand is crucial for understanding future resource requirements.
-
Are there alternatives to rare earth minerals in some applications?
Yes, research and development efforts are underway to find alternative materials that can replace rare earth minerals in certain applications. For example, some companies are exploring the use of alternative magnet technologies that do not rely on rare earth elements. However, these alternatives often have performance limitations or are more expensive, so the widespread adoption of substitutes remains a challenge.
-
How is rare earth mineral recycling being developed and what impact could it have?
Rare earth mineral recycling is gaining increasing attention as a strategy to reduce dependence on primary mining and minimize environmental impact. Recycling involves extracting rare earth elements from end-of-life products, such as electronics, magnets, and batteries. Technological advancements in recycling processes are improving efficiency and reducing costs. Widespread adoption of recycling could significantly decrease the need for new mining, alleviate supply chain pressures, and promote a more circular economy for rare earth minerals.
-
What are the geopolitical implications of rare earth mineral control?
The control of rare earth minerals carries significant geopolitical weight. Countries that possess substantial rare earth reserves or dominate the processing stages can exert influence over other nations dependent on these materials for their industries. This can lead to strategic alliances, trade negotiations, and, in some cases, political leverage. The U.S. and other nations are actively seeking to diversify their rare earth sources to reduce vulnerability to potential supply disruptions or political pressures from dominant players.
-
How does the rare earth minerals industry impact the environment and what measures are being taken to mitigate these impacts?
The rare earth minerals industry is associated with several environmental concerns, including water and soil contamination from mining and processing chemicals, habitat destruction, and radioactive waste generation. Efforts to mitigate these impacts involve implementing stricter environmental regulations, developing more eco-friendly extraction and processing techniques (such as bioleaching), promoting recycling and reuse of rare earths, and investing in waste management and remediation technologies. Sustainable and responsible practices are crucial to minimize the ecological footprint of the rare earth mineral industry.
-
What new technologies and innovations are being developed in the rare earth industry?
The rare earth industry is experiencing significant innovation in various areas. These include:
- Enhanced mining techniques to reduce environmental damage.
- More efficient and cleaner processing methods.
- Advanced recycling technologies for recovering rare earths from waste streams.
- Development of alternative materials to reduce reliance on rare earths.
- Improved supply chain management and traceability systems.
These innovations aim to improve the sustainability, efficiency, and security of the rare earth mineral supply chain.
-
What role do government regulations play in the rare earth industry?
Government regulations are crucial for governing the rare earth industry to ensure environmental protection, worker safety, and responsible mining practices. Regulations can cover various aspects, including:
- Permitting and licensing of mining operations.
- Environmental standards for water and air quality.
- Waste management and disposal requirements.
- Labor standards and worker safety protocols.
- Supply chain transparency and traceability.
Effective regulations help promote sustainable and ethical practices within the rare earth industry.
-
How does consumer demand impact the rare earth minerals industry?
Consumer demand plays a significant role in shaping the rare earth mineral industry. Increasing consumer demand for electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy technologies drives up the demand for rare earths. Consumers are also becoming more aware of the environmental and social impacts of the products they purchase. This awareness can influence purchasing decisions and drive demand for products made with recycled materials or produced using sustainable practices, thereby encouraging more responsible practices in the rare earth industry.
-
What are the long-term trends and future outlook for the rare earth market?
The long-term trends and future outlook for the rare earth market include:
- Increasing demand driven by growth in electronics, EVs, and renewable energy.
- Greater emphasis on supply chain diversification and security.
- Growing focus on recycling and alternative materials.
- Stricter environmental regulations and sustainable practices.
- Continued innovation in mining, processing, and recycling technologies.
- Potential for geopolitical tensions and trade disputes to influence market dynamics.
The rare earth market is expected to remain strategically important, and its future will depend on technological advancements, government policies, and geopolitical factors.